Mechanism of Action
Current theories on the pathogenesis of the cognitive signs and symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease attribute some of them to a deficiency of cholinergic neurotransmission. Donepezil hydrochloride is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase. There is no evidence that donepezil alters the course of the underlying dementing process.
Clinical Studies
The effectiveness of Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets as a treatment for moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease compared to donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg has been demonstrated by the results of a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical investigation in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. The controlled clinical study was conducted globally in patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-IV criteria, MMSE: range of 0-20. Patients were required to have been on a stable dose of Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 10 mg/day for at least 3 months prior to screening.
One thousand four hundred and thirty four (1434) patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease were randomized to 23 mg/day or 10 mg/day. The mean age of patients was 73.8 years, with a range of 47 to 90. Approximately 63% of patients were women, and 37% were men. Approximately 36% of the patients were taking memantine throughout the study.
Study Outcome Measures: The effectiveness of treatment with Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets was determined using a dual outcome assessment strategy that evaluated cognitive function using an instrument designed for more impaired patients and overall function through caregiver-rated assessment. The ability of Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB). The SIB, a multiitem instrument, has been validated for the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with moderate to severe dementia. The SIB evaluates selective aspects of cognitive performance, including elements of memory, language, orientation, attention, praxis, visuospatial ability, construction, and social interaction. The SIB scoring range is from 0 to 100, with lower scores indicating greater cognitive impairment.
The ability of Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using a Clinician’s Interview-Based Impression of Change that incorporated the use of caregiver information, the CIBIC-plus. The CIBIC-plus used in this trial was a semi-structured instrument that examines four major areas of patient function: General, Cognitive, Behavioral and Activities of Daily Living. It represents the assessment of a skilled clinician based upon his/her observations at an interview with the patient, in combination with information supplied by a caregiver familiar with the behavior of the patient over the interval rated. The CIBIC-plus is scored as a seven point categorical rating, ranging from a score of 1, indicating “markedly improved,” to a score of 4, indicating “no change” to a score of 7, indicating “markedly worse.”
Effects on the SIB: Figure 1 shows the time course for the change from baseline in SIB score for the two treatment groups over the 24 weeks of the study. At 24 weeks of treatment, the LS mean difference in the SIB change scores for Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets treated patients compared to patients treated with 10 mg donepezil was 2.2 units (p =0.0001). Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets /day was statistically significantly superior to 10 mg/day donepezil.
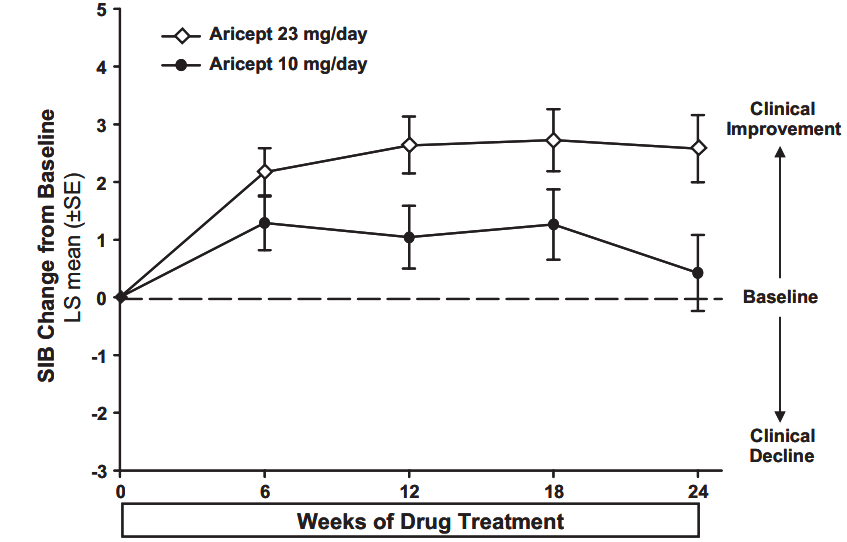 Figure 1. Time-course of the Change from Baseline in SIB Score for Patients Completing 24 Weeks of Treatment.
Figure 1. Time-course of the Change from Baseline in SIB Score for Patients Completing 24 Weeks of Treatment.
Figure 2 illustrates the cumulative percentages of patients from each of the two treatment groups who attained the measure of improvement in SIB score shown on the X-axis. While patients assigned both to Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets and to donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg tablets have a wide range of responses, the curves show that the Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets group is more likely to show a greater improvement in cognitive performance. When such curves are shifted to the left, this indicates a greater percentage of patients responding to treatment on the SIB.
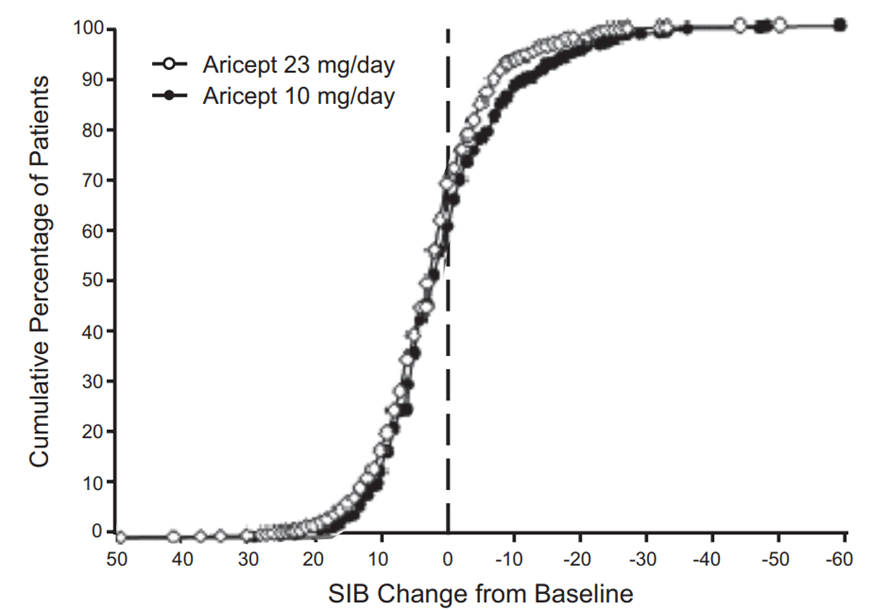 Figure 2. Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 24 Weeks of Double-blind Treatment with Specified Changes from Baseline SIB Scores
Figure 2. Cumulative Percentage of Patients Completing 24 Weeks of Double-blind Treatment with Specified Changes from Baseline SIB Scores
Effects on the CIBIC-plus:
Figure 3 is a histogram of the frequency distribution of CIBIC-plus scores attained by patients at the end of 24 weeks of treatment. The mean difference between Donepezil hydrochloride (ARICEPT®) 23 mg tablets mg and donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg tablets was 0.06 units. This difference was not statistically significant.
 Figure 3. Frequency Distribution of CIBIC plus Scores at Week 24
Figure 3. Frequency Distribution of CIBIC plus Scores at Week 24

