| Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion | Special Population | Other Details |
Absorption
After single and multiple oral administrations to Japanese healthy adult subjects under fasted condition, safinamide was rapidly absorbed with a tmax of 1.0 to 3.5 hours. In addition, when healthy adult subjects received a single oral dose of safinamide 50 mg, the bioavailability was 95% (non-Japanese data).
A comparison of plasma pharmacokinetic parameters (Cmax, tmax, t1/2, and AUC0-t) in Japanese healthy adult subjects (n=8) who received a single oral dose of safinamide 50 mg under fasted and fed conditions showed no food effect.
Blood Level
Single dose
When Japanese healthy adult subjects received single oral doses of safinamide 50, 100, and 200 mg under fasted condition, plasma concentrations of safinamide over time and plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of safinamide were as follows.
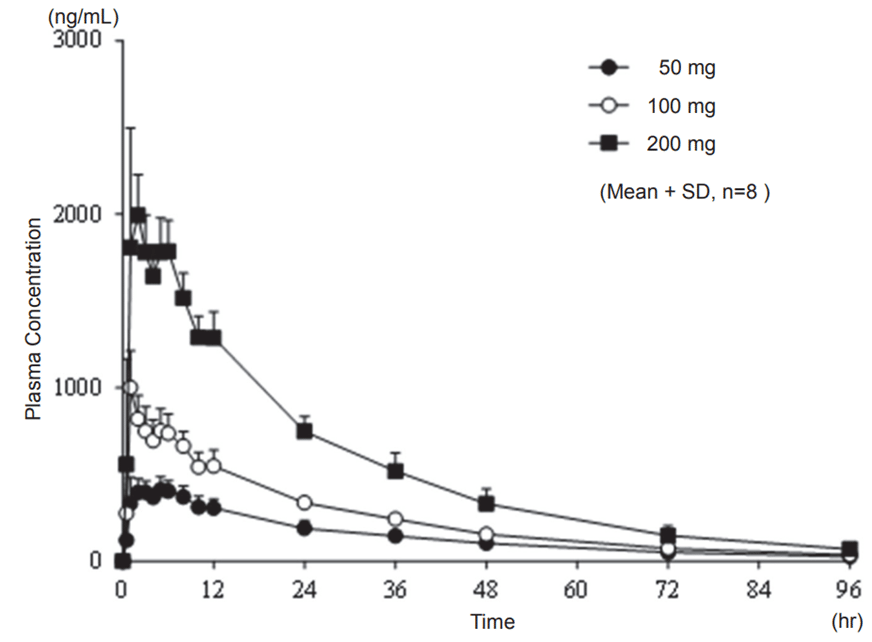
Figure 1 Plasma Concentrations of Safinamide Over Time after Single Oral Administration under Fasted Condition in Japanese Healthy Adult Subjects
Table 1 Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Safinamide after Single Oral Administration under Fasted Condition in Japanese Healthy Adult Subjects
| Dose | Number of Subjects Evaluated |
tmaxa (hr) | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC0–∞ (ng·hr/mL) | t1/2 (hr) |
| 50 mg | 8 | 3.5 (1.0 – 6.0) | 463.02 ± 52.54 | 14343.2 ± 3085.4 | 24.16 ± 2.37 |
| 100 mg | 8 | 1.0 (1.0 – 5.0) | 1006.71 ± 209.13 | 24440.0 ± 2178.2 | 22.39 ± 2.36 |
| 200 mg | 8 | 1.5 (1.0 – 5.0) | 2172.88 ± 298.69 | 53845.3 ± 8751.0 | 20.44 ± 2.85 |
a: Median and range (minimum – maximum) Mean±SD Note: The approved daily dose of this drug is generally 50 mg and the maximum is 100 mg.
Multiple doses
When Japanese healthy adult subjects received multiple oral doses of safinamide 50, 100, and 200 mg once daily for 7 days under fed condition (under fasted condition on Day 7 only), plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of safinamide after the last dose were as follows. Cmax and AUC after multiple doses of safinamide increased dose-proportionally. The accumulation ratio for Cmax and AUC0-24 (Day 7/Day 1) ranged 1.9 to 2.0, and no accumulation occurred at any doses, and the steady state was reached by Day 6 of treatment.
Table 2 Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Safinamide after Multiple Oral Administration in Japanese Healthy Adult Subjects
| Dose (Number of Subjects Evaluated) |
Day | tmaxa (hr) | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUC0–24h (ng·hr/mL) | t1/2 (hr) |
| 50 mg (8) |
1 | 3.0 (0.5 – 4.0) | 398.51 ± 72.98 | 5 647.5 ± 793.8 | 18.67 ± 2.97 |
| 7 | 1.0 (1.0 – 6.0) | 745.84 ± 93.40 | 11 434.4 ± 1 758.3 | 21.61 ± 1.92 | |
| 100 mg (7) |
1 | 4.0 (3.0 – 5.0) | 936.06 ± 154.02 | 13 989.5 ± 2 325.7 | 18.90 ± 3.52 |
| 7 | 1.0 (0.5 – 6.0) | 1 819.01 ± 451.92 | 28 754.7 ± 7 215.5 | 21.56 ± 2.91 | |
| 200 mg (8) |
1 | 3.0 (2.0 – 4.0) | 1 842.86 ± 214.24 | 26 595.0 ± 2 479.9 | 18.16 ± 1.45 |
| 7 | 1.0 (1.0 – 5.0) | 3 632.43 ± 547.66 | 53 976.0 ± 5 553.3 | 20.39 ± 2.16 |
a: Median and range (minimum – maximum) Mean ± SD Note: The approved daily dose of this drug is generally 50 mg and the maximum is 100 mg.
Distribution
When healthy adult subjects received a single intravenous dose of safinamide 50 mg, the distribution volume was 165 L (non-Japanese data). The plasma protein binding in humans was 89% (in vitro).
Metabolism
The main elimination pathway of safinamide is metabolism. It was suggested that safinamide is metabolized by nonspecific cytoplasm amidase and CYP3A4, and MAO-A and aldehyde dehydrogenase are involved in the metabolism of intermediate products. It was estimated that the contribution of nonmicrosomal enzymes (cytoplasm amidase/MAO-A) might be greater than that of CYP3A4 to safinamide metabolic capacity (in vitro, non-Japanese data).
Excretion
When healthy adult subjects received a single oral dose of 14C-safinamide 400 mg, 78% of total radioactivity was excreted (76% in urine and 1.5% in feces). A trace of unchanged safinamide was excreted in urine within 48 hours after administration, indicating that most of the administered safinamide is metabolized (non-Japanese data).
When Japanese healthy adult subjects received single oral doses of safinamide 50, 100, and 200 mg, 4.5% to 4.9% was excreted unchanged in urine by 96 hours after administration, and the cumulative urinary excretion rate of metabolites up to 96 hours after administration was 31.5% to 34.3% for propionate metabolite, 0.22% to 0.25% for benzoate metabolite, and 28.4% to 32.8% for glucuronate conjugate.
Note) The approved daily dose of this drug is generally 50 mg and the maximum is 100 mg.
Special Population
Patients with Renal Impairment
When subjects with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min) and subjects with severe renal impairment (eGFR of less than 30 mL/min and not requiring hemodialysis) received a single oral dose of safinamide 50 mg, plasma pharmacokinetic parameters were similar to those of subjects with normal renal function (eGFR of more than 90 mL/min) (non-Japanese data).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
When subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A and B) received a single oral dose of safinamide 50 mg, AUC0-∞ was increased by 32% and 82%, respectively, compared with subjects with normal hepatic function (non-Japanese data).
Other details
Drug-Drug Interaction
Ketoconazole
When healthy adult subjects (n=14) received a multiple dose of ketoconazole (CYP3A4 inhibitor) 200 mg twice daily for 6 days and a single dose of safinamide 100 mg, Cmax and AUC0-∞ were increased by 6.6% and 12.9%, respectively, compared with safinamide alone (non-Japanese data).
Midazolam
When healthy adult subjects (n=16) received a multiple dose of safinamide 100 mg once daily for 14 days and a single dose of midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate) 7.5 mg, Cmax and AUC0-t were decreased by 2% and 20%, respectively, compared with midazolam alone (non-Japanese data).
Caffeine
When healthy adult subjects (n=16) received a multiple dose of safinamide 100 mg once daily for 14 days and a single dose of caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate) 200 mg, Cmax and AUC0-t were increased by 7% and 13%, respectively, compared with caffeine alone (non-Japanese data).
Rosuvastatin
When healthy adult subjects (n=24) received a multiple dose of safinamide 100 mg once daily for 11 days and a single dose of rosuvastatin calcium (BCRP substrate) 20 mg, Cmax and AUC0-t were increased by 29% and 21%, respectively, compared with rosuvastatin calcium alone (non-Japanese data).
Levodopa/Carbidopa
When patients with Parkinson’s disease (n=24) received multiple dose of safinamide 100 mg once daily for 6 days in combination with levodopa/carbidopa, Cmax and AUC0-6 of levodopa were decreased by 0.6% and 7.2%, respectively, compared with levodopa/carbidopa alone (non-Japanese data).
Induction of CYP
In an enzyme induction study using human hepatocytes, safinamide at concentrations of ≥1 μM led to a ≥2-fold increase in CYP2B6 mRNA expression compared with a control, suggesting possible induction of CYP2B6 by safinamide (in vitro).

